
First, some facts. Of the Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering graduates we've analyzed , here's how many have used (or NOT used) their degree in their career:
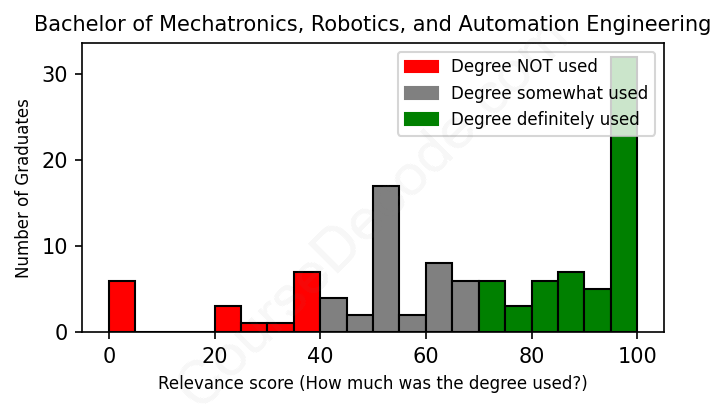
These are estimates based on AI analysis of 116 LinkedIn profiles (see below).
The verdict? Slightly above average. Overall, with an average relevance score of 68%, Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering graduates have a slightly higher likelihood (+1%) of finding work in this field compared to the average graduate across all fields:
And for comparison, here's the chart for all profiles we've looked at across all degrees.
Also, after graduating, 44% of these graduates have pursued further education other than another Bachelor's degree (such as a Masters degree or other), compared to the average across all profiles of 35%. This suggests you may need more than just a Bachelors degree to be competitive as a Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering graduate.
See the details:
|
Relevance score: 61% We think this person has gone into a career only somewhat relevant to their degree. We think this person has gone into a career only somewhat relevant to their degree.
DEGREE INFOGraduated in 2012 from Simon Fraser University with a Bachelor of Applied Science (B.A.Sc.) in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering. No other secondary education since. JOB HISTORY SINCE GRADUATIONProject Manager Noura Construction Nov 2012 - Sep 2021 Vice President Operations  Solaxy Group Corp. Nov 2021 - Present ABOUTHighly motivated & business minded. |
The top 10 most common jobs done by the graduates we've analyzed (ranked most common to least) are:
After gathering and analyzing the career paths of graduates with a degree in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering, a clear trend emerges regarding the types of jobs they end up in and their relevance to their field of study. Many graduates find roles that are indeed closely aligned with their educational background, especially in engineering-focused positions. A significant portion of graduates works as engineers or specialists in fields that directly apply mechatronics principles, including roles such as Robotics Engineer, R&D Engineer, and Automation Engineer. These positions not only employ the technical skills learned during their studies but also evolve with the graduate's career, often moving into roles that require advanced engineering knowledge and leadership skills.
However, it’s important to note that not all job placements are directly related to Mechatronics. Some graduates take on roles that emphasize management, sales, or consultancy, where the core engineering skills of mechatronics aren't utilized extensively. Positions like Business Development Manager and Applications Support Engineer highlight this trend, where the focus often shifts from technical engineering tasks to managing client relationships or product strategy. While these roles may benefit from a mechatronics background, they do not primarily require the specific technical skills that were the focus of their degree. Furthermore, there are also examples of graduates working in jobs completely unrelated to their field, involving tasks such as customer service, sales, and project management, which indicates that while a degree in Mechatronics opens many doors, it doesn’t guarantee a career centered on its technical disciplines.
In conclusion, while a majority of Mechatronics graduates find relevant and technical positions that align with their degree, a substantial number also explore opportunities outside their direct field of expertise. The variety in job relevance demonstrates the flexibility and diverse skill set that a Mechatronics education provides, allowing graduates to navigate different career paths, even if those do not heavily utilize their technical training. It’s this adaptability in skills that can make a Mechatronics degree valuable, but it also underscores the need for graduates to seek roles that more closely align with their educational background and career aspirations.
Here is a visual representation of the most common words in job titles for Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering graduates:
Looking at the career trajectories of individuals who have graduated with degrees in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering, it seems there is a mix of success stories as well as some less traditional pathways. Many of these graduates kick-start their careers with positions that are directly related to their studies, such as internships in engineering or research roles. For instance, graduates starting as engineering interns at well-known companies typically showcases that they are entering positions that align well with their educational backgrounds. Over time, they often transition into more advanced roles, such as engineers or project managers, within the engineering field. From internships in companies like Tesla to positions as R&D engineers, a significant number of graduates appear to establish careers that are relevant to technology and engineering sectors right after graduation.
Fast forward a few years, and what stands out is that many of these alumni seem to move up the ranks or diversify their skill sets. Numerous graduates have built robust careers as senior engineers, project managers, or even directors of engineering. For example, some alumni who started in internships or as entry-level engineers have been promoted to leadership roles in their respective companies, marking a clear sign of career advancement. However, it’s important to note that not all graduates follow a linear path in their careers, with some shifting towards business development, sales, or even education roles. It’s certainly telling that while many graduates strive to stay within technical roles where they can apply their Mechatronics knowledge, some shift into areas that leverage their skills in new ways, possibly showing a versatility in their training. Overall, even though a decent number find careers directly in their field, there is also a noticeable portion that ends up in roles that may not initially seem related to Mechatronics, indicating differing personal choices and opportunities that arise.
In conclusion, graduates in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering often begin with strong, relevant early-career positions that align closely with their degrees. As they progress, many ascend to more senior technical roles, while some venture into diverse fields. The data indicates a general success trend in achieving significant roles within engineering or related domains, but there’s room for improvement regarding the number who utilize their degrees in traditional engineering paths. Ultimately, the career trajectories of these graduates showcase a blend of both solid foundational employment and some unpredictability in job alignment with their areas of study.
A Bachelor’s degree in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering is generally considered to be on the tougher side compared to average degrees, but that doesn’t mean it’s impossible! You’ll dive into a mix of mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering, which means you’ll be tackling lots of math, physics, and programming. If you enjoy hands-on projects and problem-solving, it can be really fun, but be ready for some challenging coursework and late nights studying for exams! Overall, it requires dedication and a bit of grit, so if you're up for it, you just might thrive in this field.
Most commonly, in the LinkedIn profiles we've looked at, it takes people 4 years to finish a Bachelor degree in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering.
Looking at these graduates, it seems like their earning potentials vary quite a bit based on their jobs and the industries they’ve entered. For example, the ones working in management positions at companies like Dewesoft and Tesla are likely pulling in some pretty decent salaries, especially considering their upward mobility over the years. On the other hand, those starting with internships or early career roles, like the graduates from NUST or the University of Michigan-Dearborn, might not be making as much initially, but they have solid foundations for future earnings as they gain experience in their respective fields.
It’s pretty clear that fields like robotics and automation can lead to lucrative careers, especially if you land roles at top-tier tech companies or engineering firms. But there are also graduates who seem to be stuck in lower-paying roles or haven’t progressed much since starting their careers. Overall, those who jumped into management or specialized technical roles at companies like Apple, Intel, or various engineering firms appear to be doing well financially, while others might not have hit their stride just yet.
Here is a visual representation of the most common words seen in the "about" section of LinkedIn profiles who have a Bachelor degree in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering. This may or may not be useful:
Here are all colleges offering a Bachelor degree in Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering (ordered by the average relevance score of their Mechatronics, Robotics, and Automation Engineering graduates, best to worst) where we have analyzed at least 10 of their graduates: